-
[Xcode12 + Swift5] 계산기 만들기 2Swift/iOS 강의 정리 2021. 4. 14. 22:09광고광고728x90
[Xcode12 + Swift5] 계산기 만들기 1
준비사항 - App Store에서 Xcode를 다운로드 받는다. 1. Xcode를 실행해서 'Create a new Xcode project'를 클릭하여 새 프로젝트를 만든다. 2. 'App' 선택 후 프로젝트의 이름을 정한다. (Interface는 Storyboa..
small-thing.tistory.com
이어서
시작하기 전
MVC 패턴에 대한 이해 필요연산자 √를 추가해보자
1. 연산 프로퍼티 사용
- 계산기 앱에 추가하려는 모든 연산은 Double 타입
- 연산자마다 Double ↔︎ String 타입을 변환해주어야 하는데 이를 간단하게 하기 위해 연산 프로퍼티를 사용
- 연산 프로퍼티를 사용하면
- 자동으로 display 안에 뭐가 있었는지를 추적하고 매번 Double 값을 String으로 바꾸지 않아도 됨
- 값을 get(가져오기)하거나 set(설정하기) 함
var displayValue: Double { get { // displayValue의 값을 가져오기 위한 코드 return Double(display.text!)! } set { // 누군가가 이 변수의 값을 설정하려고 할 때 실행되는 코드 display.text = String(newValue) } }- displayValue 변수가 값을 가진다면, display가 Double일 때의 값이 될 것임
- 또, displayValue 변수에 값을 넣어준다면 display를 set 해주었다고 할 수 있음
- get
- display의 text를 반환받기 때문에 String → Double로 변환 return Double(display.text!)
- 변환이 안 될 지도 모르기 때문에 옵셔널임 → 강제 언래핑 return Double(display.text!)!
- 이는 display에 항상 숫자만 입력받을 거라고 가정하는 코드를 짠 것임
- set
- newValue는 누군가가 set한 Double 타입의 값
- displayValue에 무언가를 넣어주었을 때의 값
- newValue는 Double → String로 변환
- Double 타입은 항상 String 타입으로 변환이 가능하기 때문에 옵셔널이 붙지 않음
💡 모든 프로퍼티가 ‘저장'만 되는 것이 아니라 ‘연산'도 될 수 있음
2. storyboard에 √ 버튼 추가 후 코드 구현
@IBAction private func performOperation(_ sender: UIButton) { userIsInTheMiddleOfTyping = false if let mathematicalSymbol = sender.currentTitle { if mathematicalSymbol == "π" { displayValue = .pi } else if mathematicalSymbol == "√" { displayValue = sqrt(displayValue) } } }✔️ √ 연산자 추가하는 방법


계산기 모델을 만들자
@IBAction private func performOperation(_ sender: UIButton) { userIsInTheMiddleOfTyping = false if let mathematicalSymbol = sender.currentTitle { if mathematicalSymbol == "π" { displayValue = .pi } else if mathematicalSymbol == "√" { displayValue = sqrt(displayValue) } } }- 위 코드는 Model 클래스로 분리해줄 것임
1. 뉴 파일 생성 CalculatorBrain.swift

- Model 파일에 절대로 UIKit을 import 하지 말기 ⇒ Model은 UI와 분리
2. CalculatorBrain 클래스 구현
import Foundation class CalculatorBrain { func setOperand(operand: Double) { } func performOperation(symbol: String) { } // Double 타입의 연산 결과가 담길 변수. 읽기전용(readOnly) var result: Double { get { return 0.0 } } }지금까지 만든 모든 메소드와 프로퍼티는 public 이었음
public - 다른 모든 클래스가 우리가 만든 클래스에 있는 모든 메소드를 불러 사용할 수 있다는 의미
private - 외부에서 호출 불가능
ViewController의 모든 코드를 private으로 수정
ViewController에 있는 코드는 Controller 내부에서만 실행될 것이고,
다른 클래스가 이것들을 호출하게 되길 원치 않으므로 private으로 수정
class ViewController: UIViewController { @IBOutlet private var display: UILabel! private var userIsInTheMiddleOfTyping: Bool = false @IBAction private func touchDigit(_ sender: UIButton) { ... } private var displayValue: Double { ... } @IBAction private func performOperation(_ sender: UIButton) { ... } }3. ViewController - Model과 Controller 연결
private var brain: CalculatorBrain = CalculatorBrain()- Controller가 Model에 접근하기 위해 brain 변수 구현
- 변수는 초기화 해야함!
performOperation 메소드 구현
@IBAction private func performOperation(_ sender: UIButton) { if userIsInTheMiddleOfTyping { brain.setOperand(operand: displayValue) //3 userIsInTheMiddleOfTyping = false } if let mathematicalSymbol = sender.currentTitle { brain.performOperation(symbol: mathematicalSymbol) //1 } displayValue = brain.result //2 }- mathematicalSymbol이 들어오게 되면 brain에게 그 symbol로 연산을 수행하기를 요청
- 연산을 수행하는 게 끝나면 display 안에 여기 있는 brain의 결과를 넣음
- 연산을 수행하는 처음 단계에서는 만약 사용자가 숫자를 입력중이라면 그 숫자를 계산기의 피연산자(operand)로 set
4. CalculatorBrain.swift 구현
- brain을 위한 데이터 구조
private var accumulator: Double = 0.0- result는 항상 현재상태의 accumulator 값
var result: Double { get { return accumulator } }- 누군가가 operand(피연산숫자)를 주면 operand로 들어오는 값으로 accumulator를 다시 set
func setOperand(operand: Double) { accumulator = operand }- 실질적인 계산을 하는 부분
func performOperation(symbol: String) { switch symbol { case "π": accumulator = .pi case "√": accumulator = sqrt(accumulator) default: break } }연산함수를 업그레이드하자 – 상수연산
- 테이블 만들기 (Dictionary)
var operations: Dictionary<String, Operation> = [ "π": .pi, "e": M_E // 자연상수 ]- Dictionary는 제네릭 타입이며, 선언을 할 때 key와 value의 타입이 무엇인지를 구체적으로 지정
- Dictionary의 초기화는 [] 대괄호를 사용
- 기존의 performOperation 함수 대신 테이블 사용
func performOperation(symbol: String) { if let constant = operations[symbol] { accumulator = constant } }- operations의 대괄호 [] 안에 찾아올 값에 해당하는 키값으로 symbol
- 왜 symbol 키로 가져온 값이 Optional Double인걸까?
- 딕셔너리는 우리가 찾으려는 키를 가지고 있지 않을 지도 모르기 때문. 따라서 없는 키를 찾을 수 없다고 nil을 반환하게 될 것임 ⇒ 강제 언래핑 ⇒ 충돌을 방지하기 위해 바인딩
연산함수를 업그레이드하자 – 단항연산
enum Operation { case Constant // 상수 case UnaryOperation // 단항연산 case BinaryOperation // 이항연산 case Equals // = }var operations: Dictionary<String, Operation> = [ "π": Operation.Constant(.pi), "e": Operation.Constant(M_E), "√": Operation.UnaryOperation(sqrt), "cos": Operation.UnaryOperation(cos), ]func performOperation(symbol: String) { if let operation = operations[symbol] { switch operation { case .Constant: break case .UnaryOperation: break case .BinaryOperation: break case .Equals: break } } }enum Operation { case Constant(Double) case UnaryOperation((Double) -> Double) case BinaryOperation case Equals }var operations: Dictionary<String, Operation> = [ "π": Operation.Constant(.pi), "e": Operation.Constant(M_E), "√": Operation.UnaryOperation(sqrt), "cos": Operation.UnaryOperation(cos) ]func performOperation(symbol: String) { if let operation = operations[symbol] { switch operation { case .Constant(let value): accumulator = value case .UnaryOperation(let function): accumulator = function(accumulator) case .BinaryOperation: break case .Equals: break } } }연산함수를 업그레이드하자 – 이항연산
enum Operation { case Constant(Double) case UnaryOperation((Double) -> Double) case BinaryOperation((Double, Double) -> Double) case Equals }var operations: Dictionary<String, Operation> = [ "π": Operation.Constant(.pi), "e": Operation.Constant(M_E), "√": Operation.UnaryOperation(sqrt), "cos": Operation.UnaryOperation(cos), "×": Operation.BinaryOperation(multiply), "=": Operation.Equals ]func multiply(op1: Double, op2: Double) -> Double { return op1 * op2 }struct PendingBinaryOperationInfo { var binaryFunction: (Double, Double) -> Double // 이항함수 var firstOperand: Double // 이항함수의 첫번째 피연산자를 추적 }private var pending: PendingBinaryOperationInfo?func performOperation(symbol: String) { if let operation = operations[symbol] { switch operation { case .Constant(let value): accumulator = value case .UnaryOperation(let function): accumulator = function(accumulator) case .BinaryOperation(let function): executePendingBinaryOperation() pending = PendingBinaryOperationInfo(binaryFunction: function, firstOperand: accumulator) case .Equals: executePendingBinaryOperation() } } }private func executePendingBinaryOperation() { if pending != nil { accumulator = pending!.binaryFunction(pending!.firstOperand, accumulator) pending = nil } }- multiply처럼 각각의 함수를 만들어주기엔 복잡함 ⇒ 클로저 사용
private var operations: Dictionary<String, Operation> = [ "π": Operation.Constant(.pi), "e": Operation.Constant(M_E), "√": Operation.UnaryOperation(sqrt), "cos": Operation.UnaryOperation(cos), "×": Operation.BinaryOperation({ $0 * $1 }), "÷": Operation.BinaryOperation({ $0 / $1 }), "+": Operation.BinaryOperation({ $0 + $1 }), "−": Operation.BinaryOperation({ $0 - $1 }), "=": Operation.Equals ]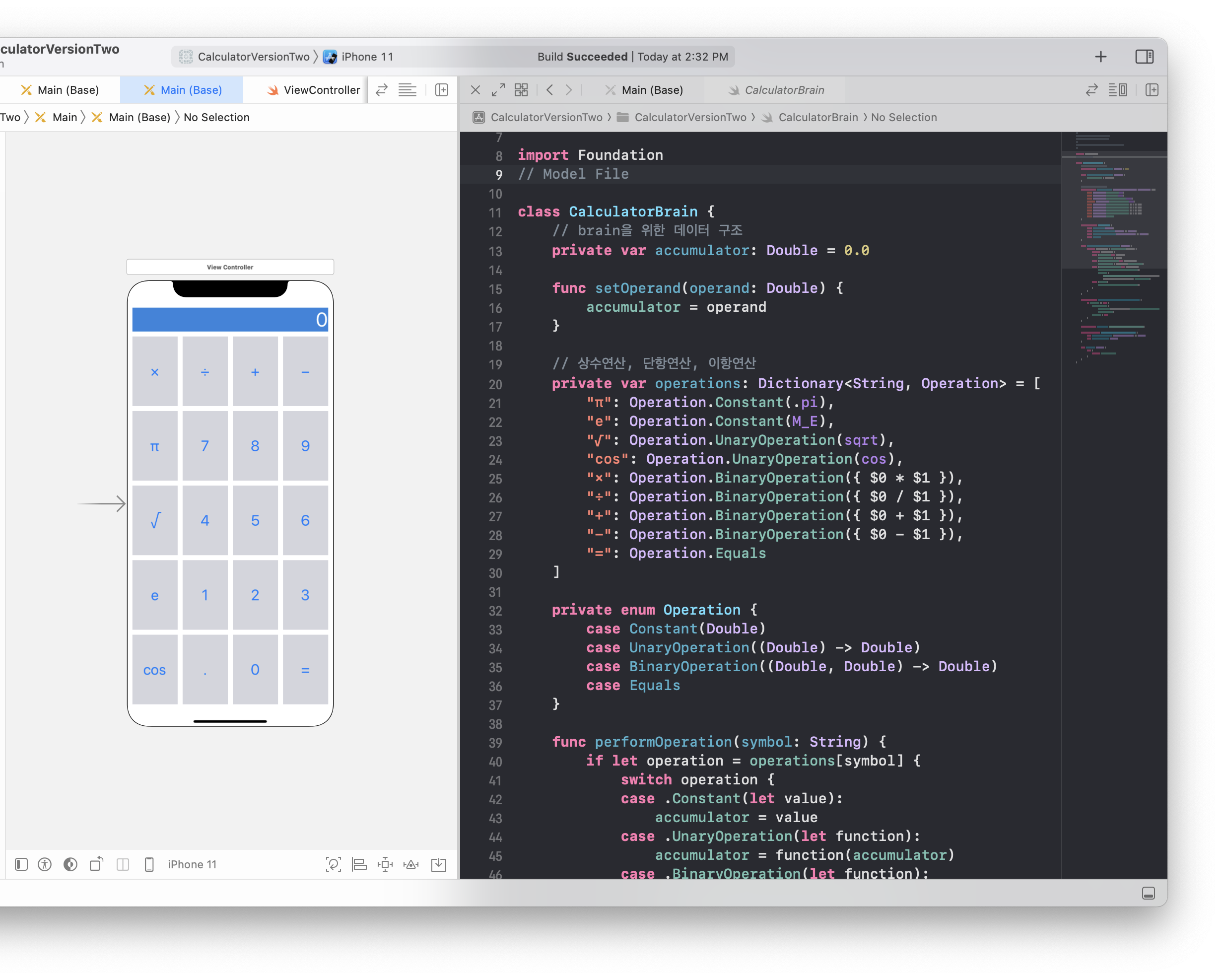
'Swift > iOS 강의 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Xcode12 + Swift5] 계산기 만들기 1 (2) 2021.04.13
